‘Outside of socialism, there is no salvation for mankind from war, hunger and the further destruction of millions and millions of human beings.’ – Vladimir Lenin
The decaying nature of capitalism meant the periods of Keynesian social democracy (1945-73) and neoliberal globalisation (1974-2016) were always unsustainable, paving the way inevitably for austerity and a rising protectionist right-wing nationalism.
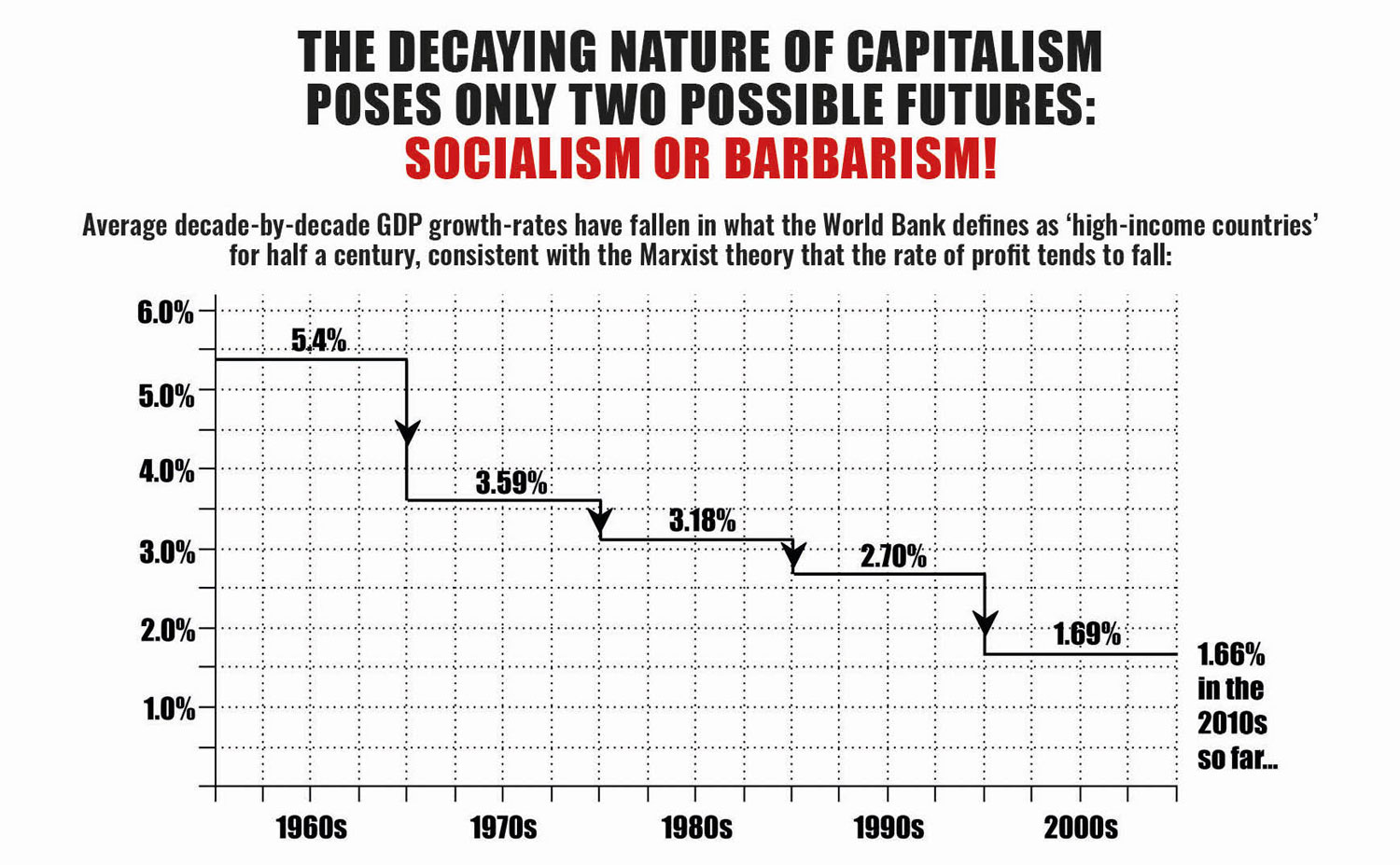
This ever-deepening crisis is grounded in the capitalist system’s tendency to produce surplus capital that cannot be reinvested profitably, creating a barrier to productivity growth, which stagnated at 0.2% in both Britain and the US in 2016. This is why interest rates are at record lows, as governments wage a futile battle to stimulate lending. In August 2016, ratings agency Fitch calculated that sovereign debt carrying negative interest rates in the global market stood at a remarkable $11.7 trillion.
Led by the US and Britain, the wars the imperialist powers are imposing on much of the world, and the resulting migration crisis, are testimony to the system’s self-destructing character. As the desperate competition for profits intensifies, the threat of devastating global conflict grows. With a record number of trade-restrictive measures implemented in 2016, the protectionism that marked the period before WW1 is inevitably returning. Protectionism will only accelerate capitalism’s decay and impoverish millions of people. There is no alternative but to fight for socialism – a planned economy serving human need instead of private profit. This is starkly demonstrated by socialist Cuba and its anti-imperialist ally Venezuela, which trade doctors for oil instead of threats of invasion and nuclear warfare.
The urgent need to rebuild the communist movement is clear.
‘We stand today before an awful proposition: either the triumph of imperialism and the destruction of all culture, and, as in ancient Rome, depopulation, desolation, degeneration, a vast cemetary; or the victory of socialsm.’ – Rosa Luxemburg

Recommended reading: Marx’s critique of political economy